Page 20
Volume 3
Journal of Nursing Research and Practice
Nursing & Immunology 2019
March 11-12, 2019
Neonatology, Pediatric Nursing and Nursing
Immunology
March 11-12, 2019 London, UK
World Congress on
8
th
World Congress on
&
Effect of inspiratory muscle training on clinical outcomes of patients undergoing cardiothoracic surgeries
Hend El-Azazy
King Saud Bin Abdulaziz University, KSA
C
ardiothoracic surgery is associated with a
significant risk of serious complications. So,
cardiothoracic surgical patients require intensive
care management postoperatively. Many of
these complications are likely caused in some
part by the exaggerated systemic inflammatory
response to Cardio-Pulmonary Bypass (CPB).
Postoperative Pulmonary Complications (PPCs)
are the most frequently observed complications
after cardiothoracic surgery, of which pneumonia
and atelectasis are the most common. PPCs have
significant clinical and economic impact associated
with increasing morbidity, length of stay and
associated cost. Inspiratory muscle training is a
therapeutic strategy that aimed at preventing post-
operative pulmonary complications. This study is
aimed to study the effect of inspiratory muscle training on clinical outcomes of patients underwent cardiothoracic surgeries. A
quasi-experimental study was conducted in Cardiothoracic Surgery Department at Student Hospital affiliated to Tanta University.
A sample of 40 adult patients of both sexes underwent cardiothoracic surgeries based on statistical power analysis were selected and
divided into 2 equal groups: Group 1 (Control Group): was received routine hospital care. Group 2 (Study Group): was received pre
and postoperative inspiratory muscle training which was implemented by the researcher. Three tools were used to collect data: Tool
(I) Cardiothoracic Patient Assessment Tool. Tool (II) Cardiovascular and Respiratory System Assessment Tool, Tool (III) Clinical
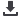
Outcome Assessment Tool. The incidence of post-operative pulmonary complications was higher in the control group (70% and
60%) while it was (30% and 25%) of the study group during the 5th and 7th post-operative day respectively. Duration of stay in ICU
was longer in the control group 4-17 days while it was 2-9 days in the study group. None of the study group compared to fifth (20%)
and fourth (25%) of the control group needed re-intubation and ICU readmission respectively. A high proportion of the study group
(55% and 70%) had dyspnea relieved by practicing of inspiratory muscle training compared to none of the study group. Inspiratory
muscle training is an effective strategy in improving patient's outcomes after cardiothoracic surgery. It was recommended that all
cardiothoracic surgical patients should receive pre and post-operative inspiratory muscle training as a daily routine care.
Biography
Hend M Elazazey is Assistant Professor in Medical Surgical Nursing Department, King Saud bin-Abdulaziz University, King of Saudi Arabia, have a more than
30 years of experience in clinical and education setting both in hospital and education institutions, has more than 20 research published papers in respected
international journals, supervised more than 8 master and PhD thesis, attended many national and international conferences.
azazeyh@ksau-hs.edu.saHend El-Azazy, J Nursing Research and Practice, Volume 3
DOI: 10.4172/2632-251X-C1-002
Fig.01