Morphometric study of sternal foramen in adult human dry sternum
Received: 10-Sep-2018 Accepted Date: Oct 03, 2018; Published: 10-Oct-2018, DOI: 10.37532/1308-4038.18.11.111
Citation: Arumugam K, Hemalatha GAJ. Morphometric study of sternal foramen in adult human dry sternum. Int J Anat Var. Dec 2018;11(4):111-114.
This open-access article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (CC BY-NC) (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits reuse, distribution and reproduction of the article, provided that the original work is properly cited and the reuse is restricted to noncommercial purposes. For commercial reuse, contact reprints@pulsus.com
Abstract
Sternal foramens are congenital defects of sternum. It develops as a result of incomplete fusion of sternabrae. This study was conducted in Department of Anatomy, Tirunelveli Medical College, Tirunelveli in 50 adult dry sternum. Our aim is to observe the presence or absence of the sternal foramen, the location, number, shape and size of the foramen. In our study 14% of sternum has sternal foramen. Single foramen is present in 5 bones, Double foraminae present in 2 bones. We review our study with previous studies. Awareness of sternal variations such as sternal foramen is important for Radiologists and in Forensic Medicine for proper interpretation. Sound knowledge about this variant is important in bone marrow aspiration and acupuncture practice to avoid complications
Keywords
Sternabrae; Foramen; Acupuncture
Introduction
The sternum or Breast bone has three parts. They are from above downwards are Manubrium (Prosternum), Body of sternum (Mesosternum) and Xiphoid process (Metasternum). Manubrium sternum has notch over upper border known as jugular notch. On either side there is an articulation facet for clavicle forming sternoclavicular joint [1-6]. On the lateral border, there are one full articular facet articulating with 1st costal cartilage forming 1st chondrosternal joint and one demi facet which articulate with the part of 2nd costal cartilage forming 2nd chodrosternal joint.
The body of the sternum articulating above with the manubrium forming manubrio-sternal joint and below articulating with the xiphoid process forming xiphi-sternal joint. The lateral border of the body of sternum have three full facet for 3rd to 6th costal cartilages and two demi facet for 2nd and 7th costal cartilages [7-12].
Body of the sternum is developed from four mesenchymal bars called as sternal bars. Chondrification of the sternal bars taking place from cranial to caudal and form sternabrae. The sternum developed from the six ossification centres. One ossification centre for manubrium, four ossification centre for body of the sternum and one for xiphoid process. The ossification centres for upper part developed earlier and subsequently proceed further downwards. Timing of appearance of ossification centres as follows, 6th IUL appear in the manubrium and 1st piece of body of sternum, 7th IUL second and third piece of body of the sternum, in the first year fourth piece of sternum and for xiphoid process ossification center developed between 5th to 18th year [13-17]. Failure of fusion of the sternabrae leads to development of sternal foramen. This is most commonly occurring in between the 3rd and 4th sternabrae. Irregular union, number and position of the ossification centers are the caused for occurrence of sternal foramen.
The morphometric study of the sternal foramen is important in Acupuncture practice and sternal marrow aspiration to prevent the damage of vital structures like pericardium and heart. Knowledge of the existence of such anatomic variants is important to avoid misdiagnosis as an osteolytic process [18-20].
Aim of the Study
• To study the presence or absence of sternal foramen.
• To study the site, size, shape and number of sternal foramen.
Methods and Materials
50 dried human adult sternums were examined grossly from Department of Anatomy, Tirunelveli Medical College, Tirunelveli for sternal foramen and their variations.
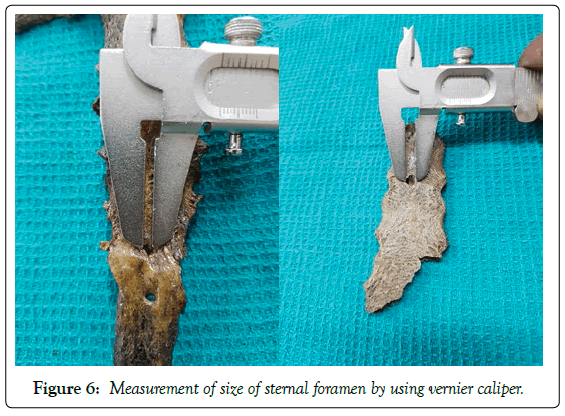
The size of the sternal foramen is measured with the help of digital vernier caliper. Photographic documentation was done.
Results
Presence or absence of sternal foramen
In our study, sternal foramen was present in 7 sternums out of 50 bones, (14%).In the remaining bones sternal foramen was absent (86%), (Table 1).
| Sl. No | Presence of sternal foramen | Absence of sternal foramen |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7 (14%) | 43 (86%) |
Table 1 Incidence of sternal foramen
Number of sternal foramina
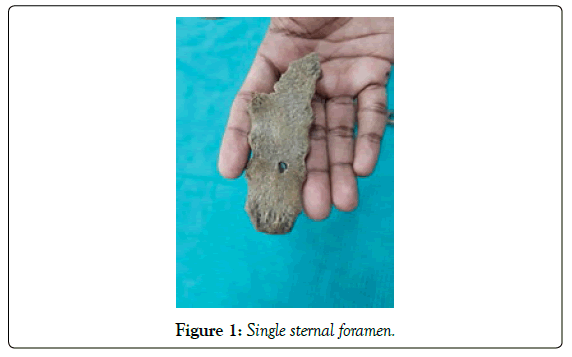
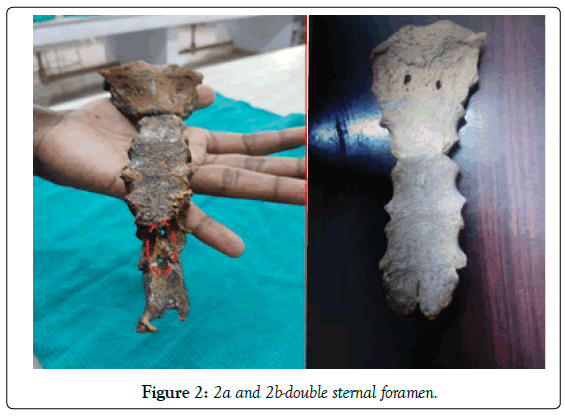
In our study single sternal foramen was noted in 5 bones. Double sternal Foraminae is present in only 2 bones (Table 2 and Figures 1, 2).
| Sl. No | Single foramen | Double foramen |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5 | 2 |
Table 2: Incidence of number of sternal foramen
Site of Sternal foramen
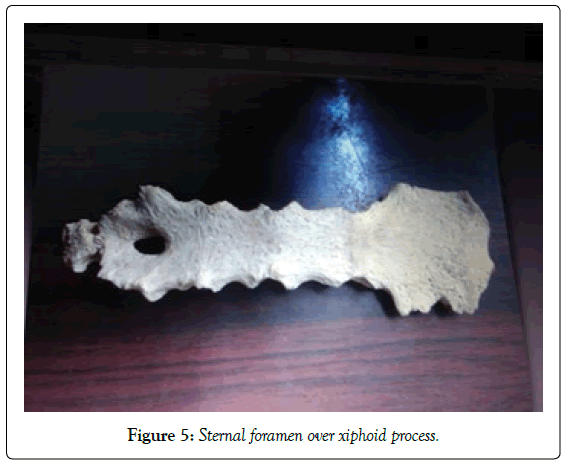
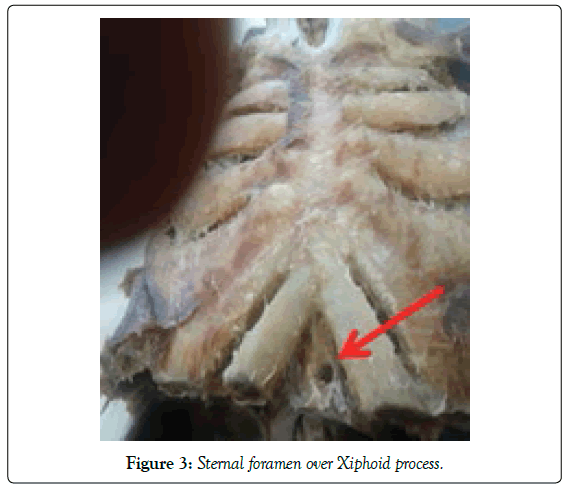
Out of 7 sternums having sternal foramen, the foramen present over manubrium in 1 bone, foramen present over the body in 3 bones, foramen seen over the xiphoid process in remaining 3 bones.
Among the 3 sternal foramen over the body of the sternum, in 2 bones, sternal foramen present at the junction of 2nd and 3rd sternal segment and in another bone present at the junction of 3rd and 4th sternal segment (Table 3).
| Sl. No | Site of sternal foramen | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Manubrium | Body of sternum | Xiphoid process | |
| 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 |
Table 3: Location of sternal foramen
The foramen present in the manubrium sternum and xiphoid process is double in number (Figures 3-5).
Shape of sternal foramen
Sternal foramen over manubrium and body of sternum is round in shape. Those over xiphoid process are oval in shape (Table 4).
| Sl. No | Shape of sternal foramen | |
|---|---|---|
| Round | Oval | |
| 1. | 4 | 3 |
Table 4: Shape of sternal foramen
Size of sternal foramen
The size of sternal foramen is measured with Vernier caliper and recorded. Sizes of all the foramens were more or less equal except in one where the size is more (40 x 5 mm) (Table 5 and Figure 6).
| Sl. No | Size of Foramen |
|---|---|
| 1. | 15 x 15 mm |
| 2. | 18 x 15 mm,10 x 5 mm |
| 3. | 20 x 10 mm |
| 4. | 10 x 10 mm |
| 5. | 40 x 5 mm |
Table 5: Size of sternal foramen
Discussion
Presence or absence of sternal foramen
Percentage of sternal foramen in present study is 14%. It is more than that of study conducted by Cooper et al. [4] (6.7%) and Gkantsinikoudis et al. [14] (6.6%) of sternal foramen in female). It is less than the findings of Paraskevas et al. [16] (18.3%), Babinski et al. [13] (16.6%), Gkantsinikoudis et al. [14] (14.2% in male), Busaid et al. [9] (13.8%) and Kirum et al. [7] (12.9%), Kumarasamy et al. [18], Kumar et al. [10] and Tandon et al. [1] in their study noted sternal foramen in only one specimen (Table 6).
| Sl. No | Name of the study | Percentage of sternal foramen (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cooper PD et al. [4] | 6.7 |
| 2. | Suba Ananthi Kumarasamy et al. [18] | 1 Specimen |
| 3. | Marcio A. Babinski et al. [13] | 16.6 |
| 4. | H.EL.Busaid et al. [9] | 13.8 |
| 5. | Paraskevas. G et al. [16] | 18.3 |
| 6. | Jithender Kumar et al. [10] | 1 Specimen |
| 7. | Aseem Tandon et al. [1] | 1 Specimen |
| 8. | N Gkantsinikoudis et al. [14] | 14.2 in male and 6.6 female |
| 9. | G.G. Kirum et al. [7] | 12.9 |
| 10. | Present study | 14 |
Table 6: Incidence of sternal foramen in different studies
Site of sternal Foramen
Gkantsinikoudis et al. [14], Busaid et al. [9] and Babinski et al. [13] studies stated that high percentage of sternums showed the sternal foramen over the body of the sternum. But in this study it is reported as only 4%.
Cooper et al. [4] stated the presence of sternal foramen in manibrium but they didn’t mention the prevalence rate. The presence of sternal foramen over the manubrium is 2% in our study which is in line with above mentioned literatures (Table 7).
| Sl. No | Name of the study | Site of sternum | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manubrium | Body of sternum | Xiphoid | Sterno-xiphoid | ||
| 1. | Cooper PD et al. [4] | Not Specified | 1 specimen | - | - |
| 2. | Suba Ananthi Kumarasamy et al. [18] | - | 1 specimen in lower one third | - | - |
| 3. | Marcio A. Babinski et al. [13] | - | 38.5% (5th segment) 64.2% (4th -5th segment) |
- | - |
| 4. | H.EL.Busaid et al. [9] | - | 81.8% (5th segment) | - | - |
| 5. | Paraskevas. G et al. [16] | - | 27.5% | 3.3% | - |
| 6. | Jithender Kumar et al. [10] | - | 1 specimen over lower third | - | - |
| 7. | Aseem Tandon et al. [1] | - | 1 specimen | - | - |
| 8. | N Gkantsinikoudis et al. [14] | - | 40% | 40% | - |
| 9. | Present study | 2% | 6% | 6% | - |
Table 7: Site of sternal foramen
Shape of sternal foramen
In a cadaveric study by Selthofer et al. [17], the longitudinal oval type was the standard shape of sternal body. Recently, in a study by Bayarogullari et al. [9] evaluated postnatal development of the sternum by MDCT; flat type was most commonly seen.
A CT study by Duraikannu et al. [6] shows a well-corticated, round to ovalshaped defect in the midline of the sternal body with an average diameter of 6 mm.
The shape of sternal foramen in the present study is oval or round similar to above mentioned previous studies (Table 8).
| Sl. No | Name of the study | Size of the foramen |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Suba Ananthi Kumarasamy et al. [18] | 20.81 x 1.42 mm |
| 2. | Marcio A. Babinski et al. [13] | 5.5 x 4.5 mm |
| 3. | Jithender Kumar et al. [10] | 18.75 x 12.50 mm |
| 4. | Aseem Tandon et al. [1] | 8.75 x 7.35 mm |
| 5. | Kosuri Kalyan Chakravarthi et al. [12] | 17 x 16 mm |
| 6. | Present study | 20 x 11 mm |
Table 8: Comparison of size of sternal foramen
Number of sternal foramina
Balta et al. [2] in his radiological study stated the incidence of double sternal foraminae in body of sternum.
In our study double sternal foramen present over the manubrium in one bone and in other specimen double foramina present in xiphoid process. Our study correlated with that of Balta et al. [2].
Cooper et al. [4] detected sternal foramina in 6.7% in autopsy population that were usually solitary and located in the body of the sternum. They also detected a foramen in the manubrium.
Vora et al. [5], in his study observed single foramen. Yekeler et al. [20] presented one single visible sternal foramen.
Our study also similar to that of findings observed by previous authors.
Size of sternal foramen
Kumarasamy et al. [18] noted the size sternal foramen to be 20.8 mm and 11.4 mm, a larger size.
Chakravarthi et al. [12] noted the highest vertical diameter of 19 mm and transverse diameter of 17 mm. Kumar et al. [10] stated the size of foramen as 18.75 x 22.50 mm. Our study is similar to the study by the above mentioned authors.
According to Yekeler et al. [20] the size of sternal foramina ranged between 2 and 16 mm, with mean of 6.5 mm. Babinski et al. [13] noted the size of foramen as 5.5 x 4.5 mm. The size of sternal foramen in our study is more than that of above mentioned authors.
Conclusion
Serious complications after sternal puncture such as cardiac tamponade and pneumothorax should be kept in mind before performing an intrinsic procedure like bone marrow biopsy acupuncture etc. It is advisable to take X-ray to rule out such variations of the sternum.
REFERENCES
- Tandon A, Garo R. Sternal foramen case report. Med J Dr. DY Patil University. 2016;9:1.
- Balta C. An anatomic abnormality: Double sternal foramina. Int J Clin Med Imaging. 2018;5.
- Chummy S. Chinnatamby, Last anatomy regional and applied. 2011;p:345.
- Cooper PD, Stawart JH, Mc Cormick WF. Development and Morphology of thr sternal foramen. American J Foren Med Pathol. 1988;9:342-7.
- Vora DH, Shah JP, Mangal HM, et al. Post mortem study of congenital anomalies of the sternum bone. NJIRM. 2014;5:37-9.
- Duraikannu C, Noronha OV, Sundarrajan P. MDCT evaluation of sternal variations: Pictorial essay. Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2016;26:185- 94.
- Kirum GG, Munabi IG, Kukiriza J, et al. Anatomical variations of the sternal angle and anomalies of adult human sterna from the Galloway osteological collection at Makerere University Anatomy Department. Folia Morphol. 2017;76:689-94.
- Standring S. The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. Gray’s Anatomy, 40th (edn), 54th chapter. 2008.
- Bayarogullari H, Yengil E, Davran R, et al. Evaluation of the postnatal development of the sternum and sternal variations using multidetector CT. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2014;20:82-9.
- Busaid HEL, Kaisha W, Hassanali J, et al. Mandela Sternal foramina and variant of xiphoid morphology in Kenyan population. Folia Morphol. 2011;71:19-22.
- Kumar J, Dhattaswall SK, Pal V. The sternal foramen: The possible forensic misinterpretation of an anatomic abnormality. J Ind Acad Foren Med. 2015;137:315-6.
- Moorer KL. Clinically oriented Anatomy.
- Chakravarthi KK, Siddaraju KS, Venumadhav N, et al. Anatomical and congenital variations of human dry sternum bone: Its embryogenesis and clinical implications. Int J Res Med Sci. 2018;6:300-4.
- Babinski MA, da Lemos L, Monique, et al. Frequency of sternal foramen evaluated by MDCI minor variation of great relevance. Surg Radiol Anat. 2014.
- Gkantsinikoudis N, Chaniotakis C, Gkasdaris G, et al. Morphological approach of the sterna foramen an Anatomic study and short review of the literature. Folia Morphol. 2016;76:484-90.
- Natsis K. Sternal foramina: Incidence in Greek population, anatomy and clinical considerations. Surg Radiol Anat. 2015;37:845-51.
- Selthofer R, Nikolić V, Mrcela T, et al. Morphometric analysis of the sternum. Coll Antropol. 2006;30:43-7.
- Kumarasamy SA, Agrawal R. A large sternal foramen. Int J Anat Var. 2011: 4: 195-6.
- Surgical Anatomy – Skandalakis. 2004.
- Yekeler E, Tunaci M, Tunaci A, et al. Frequency of sternal variations and anomalies evaluated by MDCT. AJR. 2006;186:956-60.