Sign up for email alert when new content gets added: Sign up
Abstract
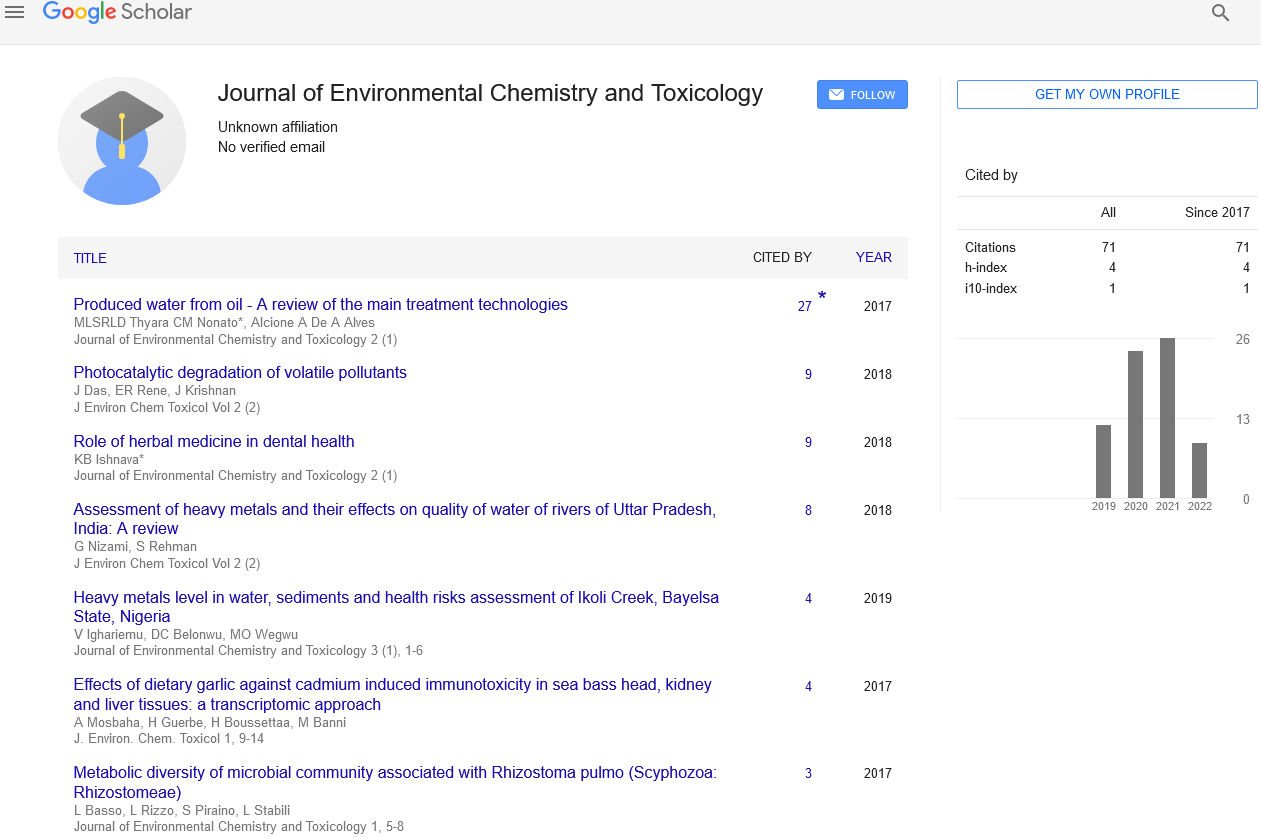
Assessment of contamination of heavy metals and pesticides in the Kosi River in District Rampur U.P
Author(s): Gulrez Nizami* and Shifa RehmanThe water pollution or contamination of surface water is currently a major area of concern of researchers due to inadequately wide expansion of urban areas and industries. The rivers are severely falling into high threats of contamination, which badly affecting the water ecosystem especially in developing countries like India. The objective of the present study is to assess the quality of Kosi river water in the basin of Rampur UP, India, for drinking and irrigation purpose. The study was carried out to determine residues of pesticide and heavy metals in water of Kosi River in Rampur to comprehend its quality. The 7 different locations were identified for the sampling of water from upstream to downstream from all the sites of Kosi in district Rampur. The samples collected were tested for organochlorine pesticide (OCP’s) and organo phosphates and heavy metals (Pb, and Hg). The evaluation of pesticides was done by GC-ECD and confirmation by GC-MS/MS. Heavy metals were analysed by Atomic absorption spectroscopy. The results showed that river water was contaminated with, DDT, chlorpyfos, Malathion , methyl paraoxon, Endosulfan-II etc. at S6 (NH24 Rampur kosi bridge) and S7 (Industrial drainage from kashipur). It was found that river water was contaminated with Aldrine (ND – 12.48 μg/l), endosulfan (ND – 13.95 μg/l), monocrotophos (ND to 3.06 μg/l), methyl paraoxon (0.01 to 259.67 μg/l) and chlopyrifos (ND to 3148.97), the heavy metals ranges: Hg (ND- 6.7975 μg/L) and Pb (10.22-44.625 μg/L) which may contribute lethal effects in the ecosystem of Kosi river. This is the first time when attempts were made to assess the quality of river by estimating the concentration of pesticides and heavy metals in this river, such work has not been conducted as before.