Sign up for email alert when new content gets added: Sign up
Psychiatric patient satisfaction scores: Improving scores by reducing mental health stigmas of health care professionals
5th World Nursing and Nursing Care Congress
March 11-12, 2019 Orlando, USA
Ruth Ann Cangialosi
Northern Kentucky University, USA
Posters & Accepted Abstracts: J Nursing Research and Practice
Abstract :
Statement of the Problem: Negative attitudes and beliefs of health care professionals towards mental illness can negatively impact patient care delivery and patient outcomes. Current literature suggests that many health care professionals have stigmas towards mental health. The broad population affected by mental health disparities includes anyone who suffers from a mental illness, including anxiety, depression, and substance abuse.
Methodology & Theoretical Orientation: A current gap in published literature exists in reducing disparities towards those with mental illness. The theoretical foundation of Peplau, Watson, and Barker, provided the foundational base that those with mental illness need to provide a patient-centered approach that is free of stigmas and bias. Quantitative methodology was utilized to observe, interpret and explain mental health stigmas amongst health care workers. A pre-test and post-test design using an established data collection tool discovered relationships between mental health stigmas and patient satisfaction scores.
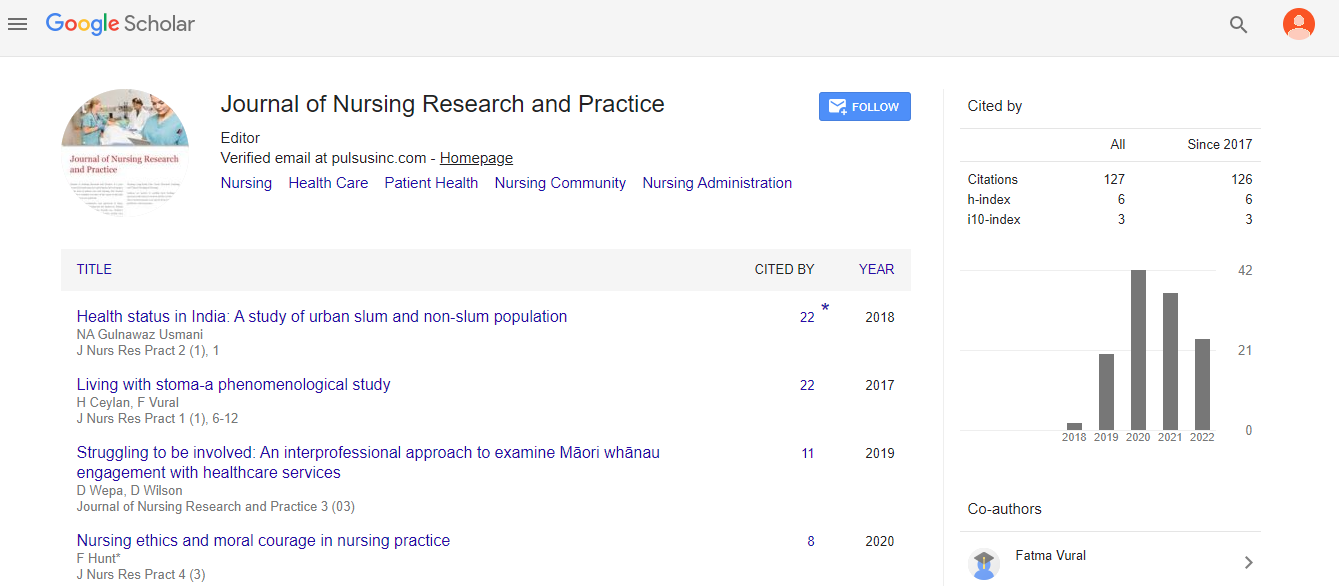
Findings: The results demonstrated that the participating healthcare providers did harbor stigmas towards mental health. Stigmas were determined from empirical literature to be detrimental to the care and outcomes for patients diagnosed with mental illness.
Conclusion & Significance: It was concluded that mental health stigmas do exist with the mental health professionals and that these stigmas negatively impact patient care and outcomes. It was also concluded that these stigmas an be reduced through staff interventions. It was shown that mental health stigmas are global in nature and pose a threat to public health, societal health, and the individual health of people.
Biography :
E-mail: dr.cangialosi@gmail.com