Mitochondrial dysfunction is the central node in the pathogenesis of renal injury in obstructive jaundice
Received: 28-Dec-2021, Manuscript No. PULJPR-21-4083; Editor assigned: 30-Dec-2021, Pre QC No. PULJPR-21-4083(PQ); Reviewed: 12-Jan-2022 QC No. PULJPR-21-4083; Revised: 28-Feb-2022, Manuscript No. PULJPR-21-4083(R); Published: 07-Mar-2022
Citation: Guixin Zhang (2022) Mitochondrial dysfunction is the central node in the pathogenesis of renal injury in obstructive jaundice. J Pharm Res. Vol: 5 No:2
This open-access article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (CC BY-NC) (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits reuse, distribution and reproduction of the article, provided that the original work is properly cited and the reuse is restricted to noncommercial purposes. For commercial reuse, contact reprints@pulsus.com
Abstract
In our latest paper, we have reviewed the underlying mechanisms, inducible agents and therapeutic strategies of kidney injury in obstructive jaundice (OJKI) [1]. Abnormal bile metabolism is the key inducement of OJKI. The kidney, as the most energy-demanding organ, requires sufficient energy to eliminate the bile and other waste in blood. About 7% of ATP energy consumption of human body is used by kidney [2]. It is closely related to the abundance of mitochondria in the renal tissue. It is doomed that mitochondria, as an important eukaryotic organelle, are of great significance to maintain the homeostasis of intracellular environment and the life activities of the organism in OJKI.
Introduction
In our latest paper, we have reviewed the underlying mechanisms, inducible agents and therapeutic strategies of kidney injury in obstructive jaundice (OJKI) [1]. Abnormal bile metabolism is the key inducement of OJKI. The kidney, as the most energy-demanding organ, requires sufficient energy to eliminate the bile and other waste in blood. About 7% of ATP energy consumption of human body is used by kidney [2]. It is closely related to the abundance of mitochondria in the renal tissue. It is doomed that mitochondria, as an important eukaryotic organelle, are of great significance to maintain the homeostasis of intracellular environment and the life activities of the organism in OJKI.
Mitochondria are organelles that hold genetic information and are primarily responsible for supplying energy and maintaining cell homeostasis[3]. It performs a wide range of tasks, including producing adenosine triphosphate, regulating calcium signaling, regulating membrane potential and controlling programmed cell death, regulating cell metabolism and proliferation, participating in cell signal transmission, and synthesizing cholesterol, which is critical for cell survival[4]. To maintain intracellular homeostasis, mitochondria must manufacture new mitochondria in a timely manner, maintain the morphology of mitochondria, and eliminate damaged mitochondria. Under pathological conditions such as stress and hypoxia, however, the disorder of mitochondrial quality control causes structural damage and dysfunction of mitochondria, such as swelling and ridge disappearance of mitochondria, decrease of membrane potential, opening of mitochondrial permeability transformation pores, ATP synthesis obstacle, excessive production of reactive oxygen free radicals, increased release of pro-apoptotic factors, and so on, which will eventually result in mitochondrial death or even cell death [5].
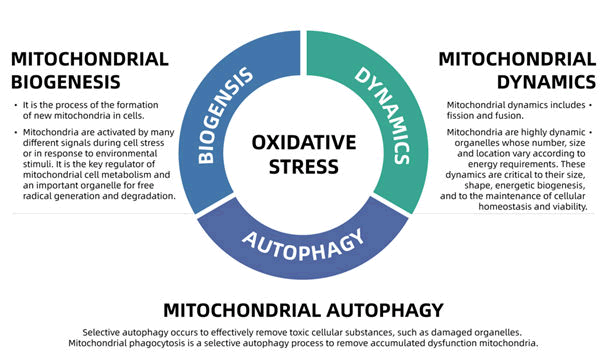
Mitochondria are extremely active organelles that maintain a constant balance of fusion and division. This dynamic equilibrium is referred to as mitochondrial dynamics. Mitochondrial homeostasis consists of the coordination of mitochondrial biogenesis, mitochondrial dynamics (including fission and fusion) and mitochondrial autophagy (Figure 1). The production of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) can be regarded as the starting factor of mitochondrial homeostasis. When ROS is produced in excess (in a state of oxidative stress), aberrant autophagy, fusion and division of mitochondria occur, resulting in mitochondrial dysfunction. Excessive ROS inhibited ATP synthesis and caused the opening of the Membrane Permeability Transition Pore (MPTP) in mitochondria, resulting in the release of cytochrome C, a shift in membrane potential, and cell death and necrosis [6].
Description
Studies have revealed the relationship between mitochondrial dysfunction and renal injury [7]. Showed that mitochondrial fragments in proximal tubule cells of kidney increase when kidney injury occurs [8]. In acute kidney injury, swelling and breakage of mitochondria in histopathology can be observed [9]. Similar phenomena can also be seen in other diseases with nephropathy as a complication. In Diabetic nephropathy, which is the most common cause of End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) in the United States, the observed variations in mitochondrial energetics are correlated with structural changes in mitochondria [10]. As a result, persistent mitochondrial dysfunction contributes to the progression of renal disorders by undermining mitochondrial homeostasis, hence impairing normal renal function.
Obviously, this is not a pathogenic phenomenon limited to a single organ or tissue. As early as studied the mitochondrial damage of kidney in rats with obstructive jaundice [11]. They found that lysosome lesion may be a possible factor of mitochondrial damage in OJKI rats. Subsequently, investigated the ultra-structural changes of isolated rat kidney induced by bilirubin and bile acid, and discovered the swelling of mitochondria and the protrusion of mitochondrial cristae [12]. In an electron microscopy study, mitochondria in kidney tissue of rats (also can be called OJKI rats) with bile duct ligation swell and rupture, even if bile returns to normal excretion, it is irreversible [13]. These studies highlight the necessity of clarifying mitochondrial dysfunction and OJKI in further research, making it a potential treatment strategy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, we believe that starting with mitochondria dysfunction could be a promising potential breakthrough for resolving OJKI. Because this is what our team observed in previous experiments (Although it has not been published yet). Based on this project, we also received support and funding from the National Natural Science Foundation of China. We also look forward to more researchers joining us on this clinical issue that deserves more attention. Finally, thank you to the editors for inviting us to provide a global platform to share our ideas and results with researchers from all over the world.
References
- Liu J, Qu J, Chen H, et al. The pathogenesis of renal injury in obstructive jaundice: A review of underlying mechanisms, inducible agents and therapeutic strategies. Pharmacol Res. 2021;163:105311.
[Crossruff] [Google Scholar] [Pubmed]
- Hoenig MP, Zeidel ML. Homeostasis, the milieu interieur, and the wisdom of the nephron. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014; 9(7):1272-81.
[Google Scholar] [Pubmed]
- Bhargava P, Schnellmann RG. Mitochondrial energetics in the kidney. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2017;13(10): 629-646.
- McBride HM, Neuspiel M, Wasiak S. Mitochondria: more than just a powerhouse. Curr Biol. 2006;16(14): R551-60.
- Ma K, Chen G, Li W, et al. Mitophagy, mitochondrial homeostasis, and cell fate. Frontiers cell develop biol. 2020;8:467
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [Pubmed]
- Lemasters JJ, Selective mitochondrial autophagy, or mitophagy, as a targeted defense against oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and aging. Rejuvenation Res. 2005; 8(1): 3-5.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [Pubmed]
- Che R, Yuan Y, Huang S, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction in the pathophysiology of renal diseases. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2014; 306(4):367-78.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [Pubmed]
- Galvan DL, Green NH, Danesh FR. The hallmarks of mitochondrial dysfunction in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2017; 92(5):1051-1057.
[Crossruff] [Google Scholar] [Pubmed]
- Emma F, Montini G, Parikh SM, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction in inherited renal disease and acute kidney injury. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2016;(5):267-280.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [Pubmed]
- Higgins GC, Coughlan MT, Mitochondrial dysfunction and mitophagy: the beginning and end to diabetic nephropathy? Br J Pharmacol. 2014; 171(8):1917-42.
- Emanuelli GG, Satta Perpignano G, Lysosomal damage and its possible relationship with mitochondrial lesion in rat kidney under obstructive jaundice. Clin Chim Acta. 1969; 25(1):167-172.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [Pubmed]
- Gollan JL, Billing BH, Huang SN, et al. Ultrastructural changes in the isolated rat kidney induced by conjugated bilirubin and bile acids. Br J Exp Pathol. 1976;57(5): 571-581.
[Google Scholar] [Pubmed]
- Ozozan OV, Dinc T, Vural V, et al. An electron microscopy study of liver and kidney damage in an experimental model of obstructive jaundice
[Google Scholar] [Pubmed]