Post-operative Recovery
"Early recovery from significant medical procedure is attractive both from the point of view of patient fulfilment, just as cost-adequacy. Drawn out medical clinic remains after medical procedure can bring about expanded horribleness, including profound vein apoplexy and nosocomial contamination, for example, pneumonia, and can quickly build emergency clinic costs and diminish repayment . All patients recuperating from significant medical procedure in gynecology and obstetrics must meet a few post-employable achievements before being released from the clinic, including enduring an eating routine, having the option to ambulate, passing flatus, voiding immediately, and sufficient agony control with oral torment prescription. So as to enable our patients to accomplish these achievements, there are numerous parts of conventional post-usable administration that must be addressed, and straightforward proof based advances that can be taken to rush momentary postoperative recovery. Tradition has directed that taking care of after medical procedure not be started until after the patient has passed flatus or has ordinary gut sounds, indicating an arrival to inside capacity. The justification for this practice was that early taking care of before come back to inside capacity was thought to bring about expanded sickness and spewing which would, in addition to causing the patient inconvenience, bring about expanded danger of desire what's more, need of nasogastric tube placement[1]. It was likewise figured that early taking care of would intensify ordinary post-usable ileus and result in declining stomach distension and wound dehiscence. However, more and more information has recommended that these assumed dangers of early feeding are unwarranted, and that early taking care of is both safe and effective in diminishing momentary post-usable recuperation time for suitable patients.
High Impact List of Articles
-
Conference Announcement: International Conference on Physicians and Surgeons
Gerald C. Hsu2020 Conference Announcement: General Surgery: Open Access
-
Conference Announcement: International Conference on Physicians and Surgeons
Gerald C. Hsu2020 Conference Announcement: General Surgery: Open Access
-
Hemobilia from rupture of pseudoaneurysm on right hepatic artery after
cholecystectomy - a case report
Fadi Rayya*, Muhammad Ghanem, Alaa Ahmad and Taisser AlmereeCase Reports: General Surgery: Open Access
-
Hemobilia from rupture of pseudoaneurysm on right hepatic artery after
cholecystectomy - a case report
Fadi Rayya*, Muhammad Ghanem, Alaa Ahmad and Taisser AlmereeCase Reports: General Surgery: Open Access
-
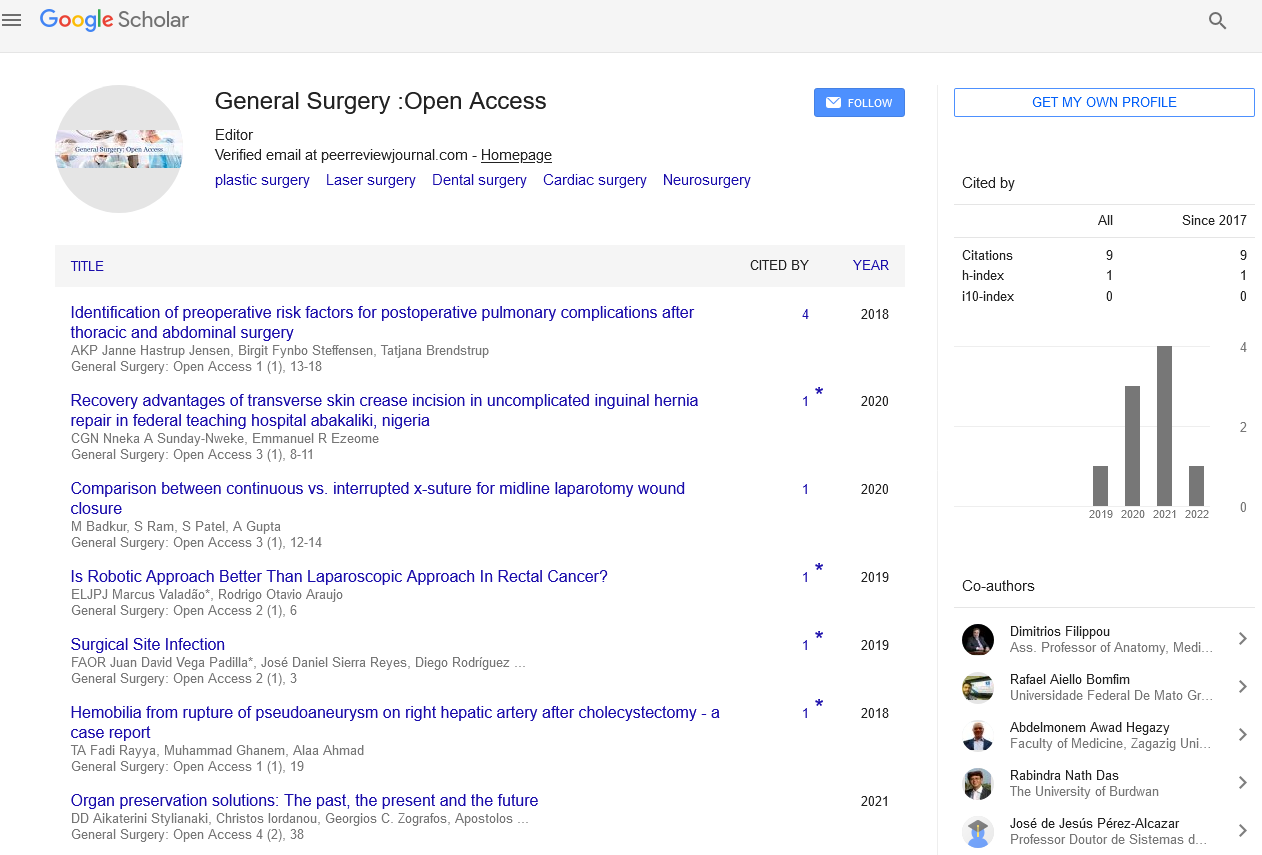
Identification of preoperative risk factors for postoperative pulmonary complications after thoracic and abdominal surgery
Janne Hastrup Jensen*, Birgit Fynbo Steffensen, Tatjana Brendstrup and Annemette Krintel PetersenResearch Article: General Surgery: Open Access
-
Identification of preoperative risk factors for postoperative pulmonary complications after thoracic and abdominal surgery
Janne Hastrup Jensen*, Birgit Fynbo Steffensen, Tatjana Brendstrup and Annemette Krintel PetersenResearch Article: General Surgery: Open Access
-
Education in cardiovascular surgery and the new technologies
Rui Almeida*Editorial: General Surgery: Open Access
-
Education in cardiovascular surgery and the new technologies
Rui Almeida*Editorial: General Surgery: Open Access
-
Idiopathic granulomatous mastitis: a disease mimics breast cancer appearing in pregnancy
Sabahattin Destek* and Vahit Onur GulCase Reports: General Surgery: Open Access
-
Idiopathic granulomatous mastitis: a disease mimics breast cancer appearing in pregnancy
Sabahattin Destek* and Vahit Onur GulCase Reports: General Surgery: Open Access
Conference Proceedings
-
Peri-procedural heart rate changes and their relation with MACE in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: Cross sectional study
Suzan LabibKeynote: Current Research: Cardiology
-
Peri-procedural heart rate changes and their relation with MACE in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: Cross sectional study
Suzan LabibKeynote: Current Research: Cardiology
-
Effect of hydrocolloid addition on properties of low-fat cheddar cheese
B K Sharma KhanalPosters & Accepted Abstracts: Applied Food Science Journal
-
Effect of hydrocolloid addition on properties of low-fat cheddar cheese
B K Sharma KhanalPosters & Accepted Abstracts: Applied Food Science Journal
-
Ethnobotanical and self- medication: Boon or Bane?
Himanshi UpadhyayaScientificTracks Abstracts: Applied Food Science Journal
-
Ethnobotanical and self- medication: Boon or Bane?
Himanshi UpadhyayaScientificTracks Abstracts: Applied Food Science Journal
-
Chitinase production from Paenibacillus sp. BISR-047 utilizing seafood waste as substrate under solid-state fermentation
Saavi PradhanPosters & Accepted Abstracts: Journal of Cancer & Metastasis Research
-
Chitinase production from Paenibacillus sp. BISR-047 utilizing seafood waste as substrate under solid-state fermentation
Saavi PradhanPosters & Accepted Abstracts: Journal of Cancer & Metastasis Research
-
Parvovirus B19 in patients of acute lymphoblastic leukemia with prolonged cytopenia
Omer Naseem, Ayishah Chaudhary, Nadia Sajid, Shahjahan and Shahida MohsinScientificTracks Abstracts: Journal of Blood Disorders and Treatment
-
Parvovirus B19 in patients of acute lymphoblastic leukemia with prolonged cytopenia
Omer Naseem, Ayishah Chaudhary, Nadia Sajid, Shahjahan and Shahida MohsinScientificTracks Abstracts: Journal of Blood Disorders and Treatment
-
Growth factors role in achieving ideal regeneration of soft and hard tissue
Ehab RashedPosters & Accepted Abstracts: Dentistry: Case Report
-
Growth factors role in achieving ideal regeneration of soft and hard tissue
Ehab RashedPosters & Accepted Abstracts: Dentistry: Case Report